Advertisement
-
Published Date
August 14, 2025This ad was originally published on this date and may contain an offer that is no longer valid. To learn more about this business and its most recent offers, click here.
Ad Text
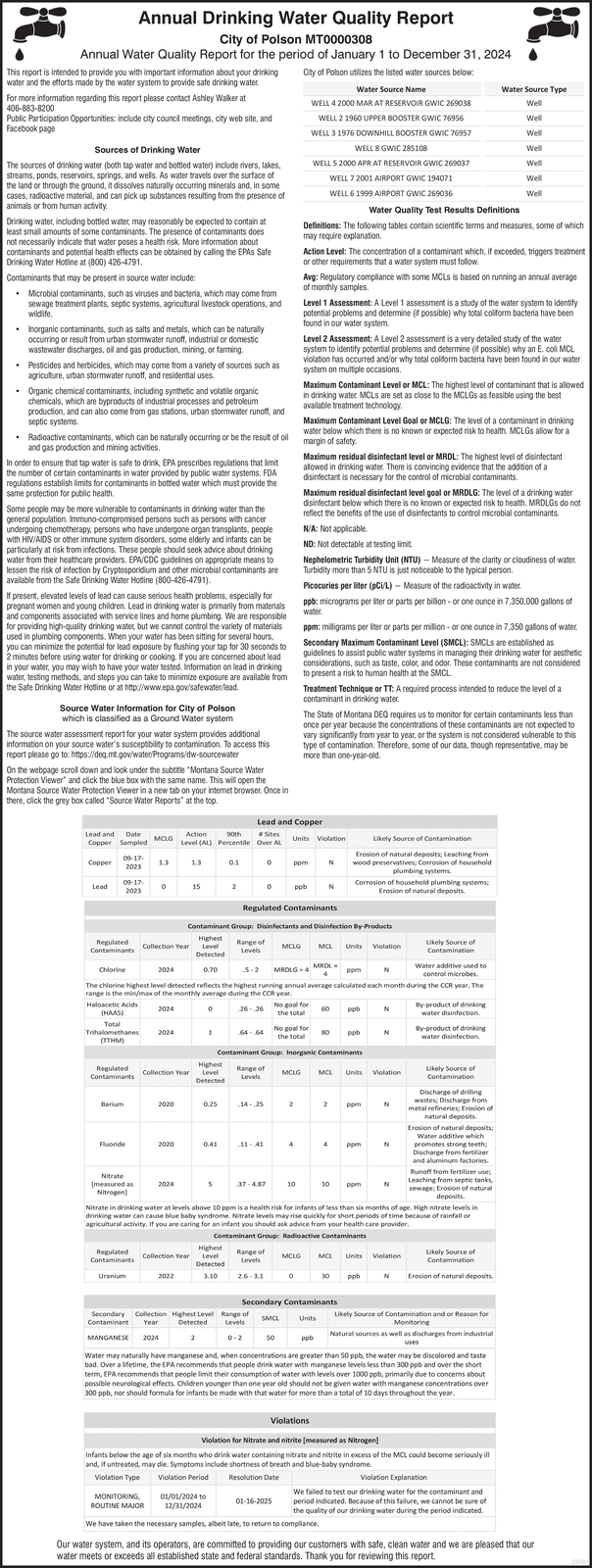
Annual Drinking Water Quality Report City of Polson MT0000308 Annual Water Quality Report for the period of January 1 to December 31, 2024 This report is intended to provide you with important information about your drinking water and the efforts made by the water system to provide safe drinking water. For more information regarding this report please contact Ashley Walker at 406-883-8200 Public Participation Opportunities: include city council meetings, city web site, and Facebook page Sources of Drinking Water The sources of drinking water (both tap water and bottled water) include rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, reservoirs, springs, and wells. As water travels over the surface of the land or through the ground, it dissolves naturally occurring minerals and, in some cases, radioactive material, and can pick up substances resulting from the presence of animals or from human activity. Drinking water, including bottled water, may reasonably be expected to contain at least small amounts of some contaminants. The presence of contaminants does not necessarily indicate that water poses a health risk. More information about contaminants and potential health effects can be obtained by calling the EPAS Safe Drinking Water Hotline at (800) 426-4791. Contaminants that may be present in source water include: Microbial contaminants, such as viruses and bacteria, which may come from sewage treatment plants, septic systems, agricultural livestock operations, and wildlife. Inorganic contaminants, such as salts and metals, which can be naturally occurring or result from urban stormwater runoff, industrial or domestic wastewater discharges, oil and gas production, mining, or farming. Pesticides and herbicides, which may come from a variety of sources such as agriculture, urban stormwater runoff, and residential uses. Organic chemical contaminants, including synthetic and volatile organic chemicals, which are byproducts of industrial processes and petroleum production, and can also come from gas stations, urban stormwater runoff, and septic systems. Radioactive contaminants, which can be naturally occurring or be the result of oil and gas production and mining activities. In order to ensure that tap water is safe to drink, EPA prescribes regulations that limit the number of certain contaminants in water provided by public water systems. FDA regulations establish limits for contaminants in bottled water which must provide the same protection for public health. Some people may be more vulnerable to contaminants in drinking water than the general population. Immuno-compromised persons such as persons with cancer undergoing chemotherapy, persons who have undergone organ transplants, people with HIV/AIDS or other immune system disorders, some elderly and infants can be particularly at risk from infections. These people should seek advice about drinking water from their healthcare providers. EPA/CDC guidelines on appropriate means to lessen the risk of infection by Cryptosporidium and other microbial contaminants are available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline (800-426-4791). If present, elevated levels of lead can cause serious health problems, especially for pregnant women and young children. Lead in drinking water is primarily from materials and components associated with service lines and home plumbing. We are responsible for providing high-quality drinking water, but we cannot control the variety of materials used in plumbing components. When your water has been sitting for several hours, you can minimize the potential for lead exposure by flushing your tap for 30 seconds to 2 minutes before using water for drinking or cooking. If you are concerned about lead in your water, you may wish to have your water tested. Information on lead in drinking water, testing methods, and steps you can take to minimize exposure are available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline or at http://www.epa.gov/safewater/lead. Source Water Information for City of Polson which is classified as a Ground Water system The source water assessment report for your water system provides additional information on your source water's susceptibility to contamination. To access this report please go to: https://deq.mt.gov/water/Programs/dw-sourcewater On the webpage scroll down and look under the subtitle "Montana Source Water Protection Viewer" and click the blue box with the same name. This will open the Montana Source Water Protection Viewer in a new tab on your internet browser. Once in there, click the grey box called "Source Water Reports" at the top. City of Polson utilizes the listed water sources below: Water Source Name WELL 4 2000 MAR AT RESERVOIR GWIC 269038 WELL 2 1960 UPPER BOOSTER GWIC 76956 WELL 3 1976 DOWNHILL BOOSTER GWIC 76957 WELL 8 GWIC 285108 WELL 5 2000 APR AT RESERVOIR GWIC 269037 WELL 7 2001 AIRPORT GWIC 194071 WELL 6 1999 AIRPORT GWIC 269036 R. Water Source Type Water Quality Test Results Definitions Well Well Well Well Well Definitions: The following tables contain scientific terms and measures, some of which may require explanation. Action Level: The concentration of a contaminant which, if exceeded, triggers treatment or other requirements that a water system must follow. Avg: Regulatory compliance with some MCLS is based on running an annual average of monthly samples. Level 1 Assessment: A Level 1 assessment is a study of the water system to identify potential problems and determine (if possible) why total coliform bacteria have been found in our water system. Level 2 Assessment: A Level 2 assessment is a very detailed study of the water system to identify potential problems and determine (if possible) why an E. coli MCL violation has occurred and/or why total coliform bacteria have been found in our water system on multiple occasions. Maximum Contaminant Level or MCL: The highest level of contaminant that is allowed in drinking water. MCLS are set as close to the MCLGS as feasible using the best available treatment technology. Maximum Contaminant Level Goal or MCLG: The level of a contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety. Maximum residual disinfectant level or MRDL: The highest level of disinfectant allowed in drinking water. There is convincing evidence that the addition of a disinfectant is necessary for the control of microbial contaminants. Maximum residual disinfectant level goal or MRDLG: The level of a drinking water disinfectant below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MRDLGs do not reflect the benefits of the use of disinfectants to control microbial contaminants. N/A: Not applicable. ND: Not detectable at testing limit. Nephelometric Turbidity Unit (NTU) - Measure of the clarity or cloudiness of water. Turbidity more than 5 NTU is just noticeable to the typical person. Picocuries per liter (pCi/L) - Measure of the radioactivity in water. ppb: micrograms per liter or parts per billion - or one ounce in 7,350,000 gallons of water. ppm: milligrams per liter or parts per million- or one ounce in 7,350 gallons of water. Secondary Maximum Contaminant Level (SMCL): SMCLS are established as guidelines to assist public water systems in managing their drinking water for aesthetic considerations, such as taste, color, and odor. These contaminants are not considered to present a risk to human health at the SMCL. Treatment Technique or TT: A required process intended to reduce the level of a contaminant in drinking water. The State of Montana DEQ requires us to monitor for certain contaminants less than once per year because the concentrations of these contaminants are not expected to vary significantly from year to year, or the system is not considered vulnerable to this type of contamination. Therefore, some of our data, though representative, may be more than one-year-old. Copper Lead and Date Copper Sampled 09-17- 2023 MCLG Lead and Copper Action 90th Sites Level (AL) Percentile Over AL Units Violation 1.3 1.3 0.1 0 ppm N Lead 15 2 ppb N Likely Source of Contamination Erosion of natural deposits; Leaching from wood preservatives; Corrosion of household plumbing systems. Corrosion of household plumbing systems; Erosion of natural deposits. Regulated Contaminants Contaminant Group: Disinfectants and Disinfection By-Products Regulated Contaminants Highest Collection Year Level Detected Range of Levels MCLG MCL Units Violation Likely Source of Contamination MRDL- Chlorine 2024 0.70 5-2 MRDLG 4 ppm N Water additive used to control microbes. The chlorine highest level detected reflects the highest running annual average calculated each month during the CCR year. The range is the min/max of the monthly average during the CCR year. Haloacetic Acids (HAAS) Total Trihalomethanes (TTHM) 2024 0 By-product of drinking water disinfection. No goal for .26-26 60 ppb N 2024 1 .64-.64 the total No goal for the total 80 ppb N By-product of drinking water disinfection. Contaminant Group: Inorganic Contaminants Regulated Contaminants Collection Year Highest Level Detected Range of Levels Likely Source of MCLG MCL Units Violation Barium 2020 0.25 14-25 2 2 ppm N Fluoride 2020 0.41 11-41 4 4 ppm N Nitrate [measured as 2024 Nitrogen] 37-4.87 10 ppm N Contamination Discharge of drilling wastes; Discharge from metal refineries; Erosion of natural deposits. Erosion of natural deposits; Water additive which promotes strong teeth; Discharge from fertilizer and aluminum factories. Runoff from fertilizer use; Leaching from septic tanks, sewage; Erosion of natural deposits. Nitrate in drinking water at levels above 10 ppm is a health risk for infants of less than six months of age. High nitrate levels in drinking water can cause blue baby syndrome. Nitrate levels may rise quickly for short periods of time because of rainfall or agricultural activity. If you are caring for an infant you should ask advice from your health care provider. Contaminant Group: Radioactive Contaminants Regulated Contaminants Uranium 2022 Highest Collection Year Level Detected 3.10 Range of Levels MCLG MCL Units Violation 2.6-3.1 30 Likely Source of Contamination N Erosion of natural deposits. MANGANESE 2024 Secondary Collection Highest Level Range of Contaminant Year Detected Levels 0-2 SMCL Secondary Contaminants Units Likely Source of Contamination and or Reason for Monitoring Natural sources as well as discharges from industrial 50 ppb uses Water may naturally have manganese and, when concentrations are greater than 50 ppb, the water may be discolored and taste bad. Over a lifetime, the EPA recommends that people drink water with manganese levels less than 300 ppb and over the short term, EPA recommends that people limit their consumption of water with levels over 1000 ppb, primarily due to concerns about possible neurological effects. Children younger than one year old should not be given water with manganese concentrations over 300 ppb, nor should formula for infants be made with that water for more than a total of 10 days throughout the year. Violations Violation for Nitrate and nitrite [measured as Nitrogen] Infants below the age of six months who drink water containing nitrate and nitrite in excess of the MCL could become seriously ill and, if untreated, may die. Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue-baby syndrome. Violation Type Violation Period MONITORING, ROUTINE MAJOR 01/01/2024 to 12/31/2024 Resolution Date 01-16-2025 Violation Explanation We failed to test our drinking water for the contaminant and period indicated. Because of this failure, we cannot be sure of the quality of our drinking water during the period indicated. We have taken the necessary samples, albeit late, to return to compliance. Our water system, and its operators, are committed to providing our customers with safe, clean water and we are pleased that our water meets or exceeds all established state and federal standards. Thank you for reviewing this report. Annual Drinking Water Quality Report City of Polson MT0000308 Annual Water Quality Report for the period of January 1 to December 31 , 2024 This report is intended to provide you with important information about your drinking water and the efforts made by the water system to provide safe drinking water . For more information regarding this report please contact Ashley Walker at 406-883-8200 Public Participation Opportunities : include city council meetings , city web site , and Facebook page Sources of Drinking Water The sources of drinking water ( both tap water and bottled water ) include rivers , lakes , streams , ponds , reservoirs , springs , and wells . As water travels over the surface of the land or through the ground , it dissolves naturally occurring minerals and , in some cases , radioactive material , and can pick up substances resulting from the presence of animals or from human activity . Drinking water , including bottled water , may reasonably be expected to contain at least small amounts of some contaminants . The presence of contaminants does not necessarily indicate that water poses a health risk . More information about contaminants and potential health effects can be obtained by calling the EPAS Safe Drinking Water Hotline at ( 800 ) 426-4791 . Contaminants that may be present in source water include : Microbial contaminants , such as viruses and bacteria , which may come from sewage treatment plants , septic systems , agricultural livestock operations , and wildlife . Inorganic contaminants , such as salts and metals , which can be naturally occurring or result from urban stormwater runoff , industrial or domestic wastewater discharges , oil and gas production , mining , or farming . Pesticides and herbicides , which may come from a variety of sources such as agriculture , urban stormwater runoff , and residential uses . Organic chemical contaminants , including synthetic and volatile organic chemicals , which are byproducts of industrial processes and petroleum production , and can also come from gas stations , urban stormwater runoff , and septic systems . Radioactive contaminants , which can be naturally occurring or be the result of oil and gas production and mining activities . In order to ensure that tap water is safe to drink , EPA prescribes regulations that limit the number of certain contaminants in water provided by public water systems . FDA regulations establish limits for contaminants in bottled water which must provide the same protection for public health . Some people may be more vulnerable to contaminants in drinking water than the general population . Immuno - compromised persons such as persons with cancer undergoing chemotherapy , persons who have undergone organ transplants , people with HIV / AIDS or other immune system disorders , some elderly and infants can be particularly at risk from infections . These people should seek advice about drinking water from their healthcare providers . EPA / CDC guidelines on appropriate means to lessen the risk of infection by Cryptosporidium and other microbial contaminants are available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline ( 800-426-4791 ) . If present , elevated levels of lead can cause serious health problems , especially for pregnant women and young children . Lead in drinking water is primarily from materials and components associated with service lines and home plumbing . We are responsible for providing high - quality drinking water , but we cannot control the variety of materials used in plumbing components . When your water has been sitting for several hours , you can minimize the potential for lead exposure by flushing your tap for 30 seconds to 2 minutes before using water for drinking or cooking . If you are concerned about lead in your water , you may wish to have your water tested . Information on lead in drinking water , testing methods , and steps you can take to minimize exposure are available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline or at http://www.epa.gov/safewater/lead . Source Water Information for City of Polson which is classified as a Ground Water system The source water assessment report for your water system provides additional information on your source water's susceptibility to contamination . To access this report please go to : https://deq.mt.gov/water/Programs/dw-sourcewater On the webpage scroll down and look under the subtitle " Montana Source Water Protection Viewer " and click the blue box with the same name . This will open the Montana Source Water Protection Viewer in a new tab on your internet browser . Once in there , click the grey box called " Source Water Reports " at the top . City of Polson utilizes the listed water sources below : Water Source Name WELL 4 2000 MAR AT RESERVOIR GWIC 269038 WELL 2 1960 UPPER BOOSTER GWIC 76956 WELL 3 1976 DOWNHILL BOOSTER GWIC 76957 WELL 8 GWIC 285108 WELL 5 2000 APR AT RESERVOIR GWIC 269037 WELL 7 2001 AIRPORT GWIC 194071 WELL 6 1999 AIRPORT GWIC 269036 R. Water Source Type Water Quality Test Results Definitions Well Well Well Well Well Definitions : The following tables contain scientific terms and measures , some of which may require explanation . Action Level : The concentration of a contaminant which , if exceeded , triggers treatment or other requirements that a water system must follow . Avg : Regulatory compliance with some MCLS is based on running an annual average of monthly samples . Level 1 Assessment : A Level 1 assessment is a study of the water system to identify potential problems and determine ( if possible ) why total coliform bacteria have been found in our water system . Level 2 Assessment : A Level 2 assessment is a very detailed study of the water system to identify potential problems and determine ( if possible ) why an E. coli MCL violation has occurred and / or why total coliform bacteria have been found in our water system on multiple occasions . Maximum Contaminant Level or MCL : The highest level of contaminant that is allowed in drinking water . MCLS are set as close to the MCLGS as feasible using the best available treatment technology . Maximum Contaminant Level Goal or MCLG : The level of a contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health . MCLGs allow for a margin of safety . Maximum residual disinfectant level or MRDL : The highest level of disinfectant allowed in drinking water . There is convincing evidence that the addition of a disinfectant is necessary for the control of microbial contaminants . Maximum residual disinfectant level goal or MRDLG : The level of a drinking water disinfectant below which there is no known or expected risk to health . MRDLGs do not reflect the benefits of the use of disinfectants to control microbial contaminants . N / A : Not applicable . ND : Not detectable at testing limit . Nephelometric Turbidity Unit ( NTU ) - Measure of the clarity or cloudiness of water . Turbidity more than 5 NTU is just noticeable to the typical person . Picocuries per liter ( pCi / L ) - Measure of the radioactivity in water . ppb : micrograms per liter or parts per billion - or one ounce in 7,350,000 gallons of water . ppm : milligrams per liter or parts per million- or one ounce in 7,350 gallons of water . Secondary Maximum Contaminant Level ( SMCL ) : SMCLS are established as guidelines to assist public water systems in managing their drinking water for aesthetic considerations , such as taste , color , and odor . These contaminants are not considered to present a risk to human health at the SMCL . Treatment Technique or TT : A required process intended to reduce the level of a contaminant in drinking water . The State of Montana DEQ requires us to monitor for certain contaminants less than once per year because the concentrations of these contaminants are not expected to vary significantly from year to year , or the system is not considered vulnerable to this type of contamination . Therefore , some of our data , though representative , may be more than one - year - old . Copper Lead and Date Copper Sampled 09-17- 2023 MCLG Lead and Copper Action 90th Sites Level ( AL ) Percentile Over AL Units Violation 1.3 1.3 0.1 0 ppm N Lead 15 2 ppb N Likely Source of Contamination Erosion of natural deposits ; Leaching from wood preservatives ; Corrosion of household plumbing systems . Corrosion of household plumbing systems ; Erosion of natural deposits . Regulated Contaminants Contaminant Group : Disinfectants and Disinfection By - Products Regulated Contaminants Highest Collection Year Level Detected Range of Levels MCLG MCL Units Violation Likely Source of Contamination MRDL- Chlorine 2024 0.70 5-2 MRDLG 4 ppm N Water additive used to control microbes . The chlorine highest level detected reflects the highest running annual average calculated each month during the CCR year . The range is the min / max of the monthly average during the CCR year . Haloacetic Acids ( HAAS ) Total Trihalomethanes ( TTHM ) 2024 0 By - product of drinking water disinfection . No goal for .26-26 60 ppb N 2024 1 .64 - .64 the total No goal for the total 80 ppb N By - product of drinking water disinfection . Contaminant Group : Inorganic Contaminants Regulated Contaminants Collection Year Highest Level Detected Range of Levels Likely Source of MCLG MCL Units Violation Barium 2020 0.25 14-25 2 2 ppm N Fluoride 2020 0.41 11-41 4 4 ppm N Nitrate [ measured as 2024 Nitrogen ] 37-4.87 10 ppm N Contamination Discharge of drilling wastes ; Discharge from metal refineries ; Erosion of natural deposits . Erosion of natural deposits ; Water additive which promotes strong teeth ; Discharge from fertilizer and aluminum factories . Runoff from fertilizer use ; Leaching from septic tanks , sewage ; Erosion of natural deposits . Nitrate in drinking water at levels above 10 ppm is a health risk for infants of less than six months of age . High nitrate levels in drinking water can cause blue baby syndrome . Nitrate levels may rise quickly for short periods of time because of rainfall or agricultural activity . If you are caring for an infant you should ask advice from your health care provider . Contaminant Group : Radioactive Contaminants Regulated Contaminants Uranium 2022 Highest Collection Year Level Detected 3.10 Range of Levels MCLG MCL Units Violation 2.6-3.1 30 Likely Source of Contamination N Erosion of natural deposits . MANGANESE 2024 Secondary Collection Highest Level Range of Contaminant Year Detected Levels 0-2 SMCL Secondary Contaminants Units Likely Source of Contamination and or Reason for Monitoring Natural sources as well as discharges from industrial 50 ppb uses Water may naturally have manganese and , when concentrations are greater than 50 ppb , the water may be discolored and taste bad . Over a lifetime , the EPA recommends that people drink water with manganese levels less than 300 ppb and over the short term , EPA recommends that people limit their consumption of water with levels over 1000 ppb , primarily due to concerns about possible neurological effects . Children younger than one year old should not be given water with manganese concentrations over 300 ppb , nor should formula for infants be made with that water for more than a total of 10 days throughout the year . Violations Violation for Nitrate and nitrite [ measured as Nitrogen ] Infants below the age of six months who drink water containing nitrate and nitrite in excess of the MCL could become seriously ill and , if untreated , may die . Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue - baby syndrome . Violation Type Violation Period MONITORING , ROUTINE MAJOR 01/01/2024 to 12/31/2024 Resolution Date 01-16-2025 Violation Explanation We failed to test our drinking water for the contaminant and period indicated . Because of this failure , we cannot be sure of the quality of our drinking water during the period indicated . We have taken the necessary samples , albeit late , to return to compliance . Our water system , and its operators , are committed to providing our customers with safe , clean water and we are pleased that our water meets or exceeds all established state and federal standards . Thank you for reviewing this report .
